The HYDROSOL-beyond project is an innovative initiative that builds upon previous HYDROSOL projects to produce renewable hydrogen from water using solar energy and redox reactions in advanced reactors. It tested various development stages, from laboratory setups to the HYDROSOL platform at the Plataforma Solar de Almeria in Spain, one of the world's largest solar research facilities. During the project, novel NiFe2O4 redox metal oxide structures were created for lab-scale water splitting and oxygen capture, demonstrating impressive stability over 1,100 cycles of hydrogen production. Additionally, a new nitrogen purification method was developed, offering potential energy savings through nitrogen recycling.
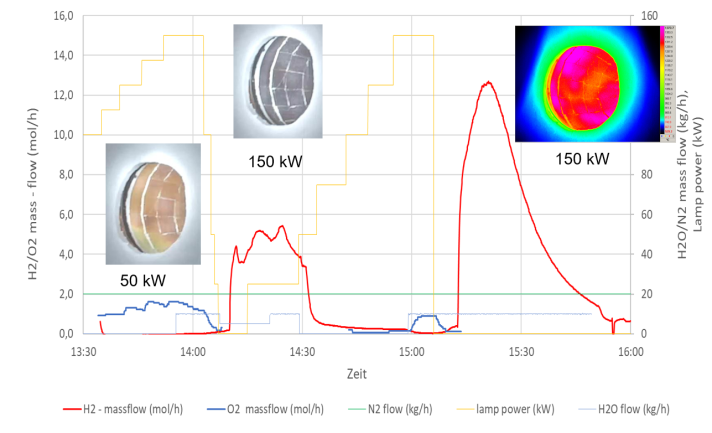
Between June 2023 and March 2024, field tests successfully operated two advanced reactor designs using NiFe2O4: an indirectly heated tube reactor filled with custom-designed NiFe2O4 lattice spheres, and a directly heated solar cavity reactor featuring NiFe2O4-coated ZrO2-foam. A hybrid ceramic-metallic heat exchanger also achieved an impressive 68% heat recovery efficiency.
HYDROSOL-beyond marks a significant advancement in producing hydrogen via high-temperature solar reactors utilizing redox reactions, as demonstrated in real-world field tests. Although performance, economic, and environmental assessments indicated the need for further optimization to enhance competitiveness and reduce environmental impact, this project showcases a successful progression from lab-scale development to real-world testing. By overcoming various technological and engineering challenges, HYDROSOL-beyond has made substantial contributions to advancing solar thermal hydrogen production and highlighting the role of demonstration projects in driving technological progress.
For more information:
Project webpage
Cordis article